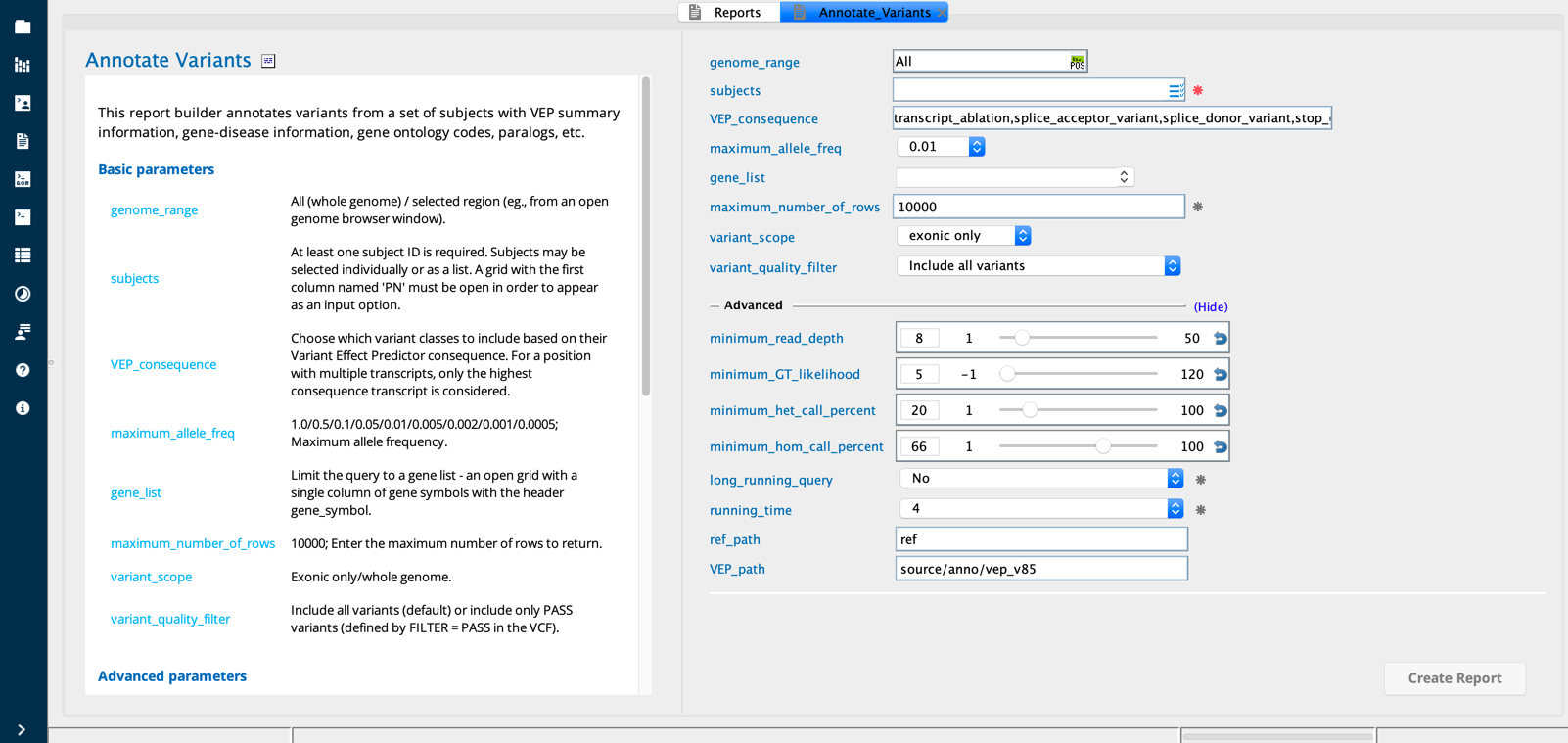
Annotate variants¶
The Annotate variants report builder annotates variants from a set of subjects with VEP summary information, gene-disease information, gene ontology codes, paralogs, etc.
The dialog generates a table of variant and gene annotations for variants meeting user defined criteria in subjects. The annotation may also be limited to variants within a set of genes of interest or within a specific genomic range.
The following annotations are added to each variant in addition to ACMG category scores:
Gene annotation from the Clinical Genome Database (CGD)
Gene annotation from European Commission project database
Gene biotype, gene ID, gene related pathway, gene parlous etc.
GO term ID and description
Genotype of each variant, call copies, call ratios, read depth, etc.
Information from public databases, such as related diseases, gene related diseases, variant related diseases, etc.
OMIM annotation of each related gene
VEP annotation of each variant, such as max_consequence, max_impact, max_score etc.
Annotate Variants in Sequence Miner¶
Example use case¶
The user wishes to annotate variants in selected subjects that meet user-defined criteria with information such as pathways, paralogs, known diseases involving each gene and clinically relevant information (from the CGD). The user also wants to identify heterozygous and homozygous variants in the subject(s).
Description of the algorithm¶
This query creates a table of variants for each input subject (PN) that meet the user’s filtering criteria (e.g., call quality, maximum impact, consequence and allele frequency of the variant). The table is then joined to annotation tables.
Variants are annotated with CAT scores. The DIAG ACMG CAT scores are calculated as follows:
If the AF > the user’s designated maxAF threshold (e.g., maxAF>0.01), then the variant is CAT4.
If the variant is not CAT4 and if MaxClinImpact is “pathogenic” (in the
ref/clinical_variants.gorzfile), then the variant is CAT1.If the variant is neither CAT4 or CAT1 and the max_impact is “HIGH” (from the
source/anno/vep_v3-4-2/vep_single_wes.gordfile), then the variant is CAT2.If the variant is neither CAT1, 2 or 4 and
if max_Consequence = “missense_variant” and max_score >= 0.9, the variant is CAT3A
OR
If max_impact = “LOW” or (max_impact = “MODERATE” and Cat3A = 0), the variant is CAT3B
Interpreting the output¶
The output table includes multiple annotation columns which are grouped by category and can be viewed in either the Default view or AMCG Perspective views. Output columns and perspectives are described below.
Column descriptions¶
Group |
Column |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Basic |
||
Call |
The actual called sequence (variant), found by replacing a part of the reference sequence and denoted by Pos and Reference, with the sequence in the Call column |
|
Chrom |
The chromosome of the variant represented as chr1, chr2, …, chr22, chrXY, chrX, chrY, chrM |
|
hetORhom |
The zygosity of the call, either “het” or “hom” |
|
PN |
The patient number (identifier) |
|
Pos |
The (first) base pair position of the sequence variant, i.e., the position of the first nucleotide in the Reference column |
|
Reference |
Sequence from the reference build, the first base starting at the base pair position in the Pos column |
Group |
Column |
Description |
|---|---|---|
CGD |
The CGD (Clinical Genome Database) columns provide information for variants based on the manually curated database of variants associated with known clinically significant conditions and available interventions. |
|
AGE_GROUP |
Pediatric: less than 18 years of age; Adult: at least 18 years of age |
|
COMMENTS |
Any additional observations noted by curators |
|
CONDITION |
Conditions also resulting from mutations in the same gene but may otherwise be placed in the “General” Intervention category |
|
INHERITANCE |
Pattern of inheritance the variant is known to follow: AD - autosomal dominant; AR - autosomal recessive; BG - blood group; Digenic - a condition resulting from simultaneous mutations in different genes; Maternal - maternal mitochondrial inheritance; XL - X-linked (because X-linked conditions can frequently have manifestations in both genetic sexes, X-linked conditions are not designated as dominant or recessive) |
|
INTERVENTION CATEGORIES |
This category includes organ systems for which specific and additional inteventions may be beneficial |
|
INTERVENTION RATIONALE |
Description of the intervention and its benefit |
|
MANIFESTATION CATEGORIES |
This category includes organ systems affected by mutations in corresponding genes; recognition of involved organ systems may help guide supportive care |
|
REFERENCES |
CGD: Clinical Genomic Database by NHGRI; PubMed ID of the reference from which the information was taken |
Group |
Column |
Description |
|---|---|---|
COMM |
The COMM columns provide variant annotation (comments) added to CSA or Sequence Miner by users |
|
CLINICAL_SIGNIFICANCE |
The clinical significance (e.g., pathogenic, benign, unknown significance, drug-response, risk factor, etc.) of the variant as annotated (commented) by users; if the same variant has several comments, this cell will contain a set of values |
|
MODE_OF_INHERITANCE |
The user-annotated (commented) mode of inheritance of the variant; if the same variant has several comments, this cell will contain a set of values |
|
TEXT |
The description (comment) component for the user annotation of the variant |
Group |
Column |
Description |
|---|---|---|
EuroGenetest |
The EuroGenetest columns are derived from a European Commission project database containing European genetic testing information for particular genes, variants, and diseases. |
|
Diseases |
Diseases associated with a variant derived from the European Commission project database |
|
NoOfDiseases |
Number of diseases associated with a variant derived from the European Commission project database |
|
NoOfpanels |
Number of gene panels associated with a variant derived from the European Commission project database |
|
panels |
EuroGenetest panels associated with a variant derived from the European Commission project database |
Group |
Column |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Gene |
The Gene columns provide information based on the candidate gene in which a variant is found. When possible, the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC) gene symbol is provided. Columns list gene annotations for the variants identified, including gene biotype, gene ID, gene related pathway, gene paralogs, etc. |
|
Aliases |
The aliases of the given gene |
|
Biotype |
Biological class of gene as annotated by VEP |
|
cdsEnd |
cDNA end position as annotated by VEP |
|
cdsStart |
cDNA start position as annotated by VEP |
|
Description |
Description of the gene, i.e., full gene name |
|
gene_stable_id |
Ensembl stable ID for the gene |
|
Paralogs |
The paralogs of the given gene |
|
Pathways |
The pathway(s) in which a given gene is found and listed in Ensembl in the |
|
Strand |
The transcription strand for the gene (+/-) |
|
Symbol |
Based on HGNC when it exists, otherwise it is the Ensembl internal alias |
Group |
Column |
Description |
|---|---|---|
GO |
The GO columns provide a functional annotation of the gene product in which the variant is found. Columns list Gene Ontology (GO) annotations for the gene, including the GO term ID and term description. |
|
Descriptions |
Gene ontology category descriptions |
|
IDs |
Gene ontology identifiers |
Group |
Column |
Description |
|---|---|---|
GT |
The GT (genotype) columns provide quality control information for the variant call based on the sequence read depth and quality. These scores are based on the Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK) measures. Columns list genotype information derived from the VCF, including the variant call, call copies, call ratio, call quality, and read depth. |
|
CallCopies |
Because the focus is only on variations from the reference, CallCopies refer to how many copies of the variation exist in a subject. A CallCopies value of “2” therefore corresponds to a homozygous variant, whereas a CallCopies value of “1” corresponds to a heterozygous variation. |
|
CallRatio |
Proportion of reads containing the variant call; expected to be close to 0.5 for heterozygous calls and close to 1 for homozygous calls |
|
Depth |
The number of reads covering the variant call |
|
FILTER |
Quality parameter using the ratio between gt-quality and depth showing if the call is considered LowQual quality (not useable) or PASS; this remains a crude quality measure |
|
GL_Call |
A statistical measure indicating the likelihood that the call is wrong; the scale has been converted to use only integers - the higher the number, the less likely it is that the call is wrong |
Group |
Column |
Description |
|---|---|---|
KNOWN |
The KNOWN columns provide publicly available information about the candidate gene and/or variant as annotated by ClinVar, HGMD, and OMIM. Columns list publicly known clinical annotations derived from ClinVar, OMIM, and HGMD Professional for the variant and gene including related diseases and predicted clinical impact. |
|
gene_diseases |
Diseases known to be associated with the gene as annotated in ClinVar, HGMD, and OMIM |
|
gene_lists |
Gene list membership of the gene in which the variant is found in the |
|
InACMG |
A Boolean column (“true” or “false”) indicating whether the gene is in the ACMG recommended list of genes for incidental findings and reporting |
|
var_diseases |
Diseases known to be associated with the variant as annotated by ClinVar, HGMD, and OMIM |
Group |
Column |
Description |
|---|---|---|
OMIM |
The OMIM columns provide the OMIM-designated identification for a particular gene and related disease description. |
|
Descriptions |
OMIM disease descriptions for the gene |
|
IDs |
The OMIM ID of the gene |
Group |
Column |
Description |
|---|---|---|
VEP |
The VEP columns provide functional annotations for variants based on the ENSEMBL SNP Effect Predictor database. Columns list Variant Effect Predictor (VEP) annotation for each variant, including the max_consequence, max_impact, max_score, and transcript information. |
|
Amino_Acids |
The amino acid with and without variant, separated by a “/” (provided only if the variant affects the protein-coding sequence), otherwise “.” |
|
max_consequence |
Consequence type reported for this variant having the greatest impact |
|
Max_Impact |
Classification of the level of severity of the transcript consequence type assigned by VEP |
|
Max_Score |
Maximum score for the variant as observed in dbNSFP [Score=max ((1-Sift_score), Polyphen2_HDIV_score, Polyphen2_HVAR_score)] |
|
Protein_Position |
Position of the amino acid in the protein sequence (only if the variant falls within a coding sequence); a value is given for each corresponding transcript specified in the CDS position field |
Group |
Column |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Other columns |
||
dbSNP_rsIDs |
The dbSNP identifier |
|
DIAG_ACMGCat |
Categorization of the sequence variants according to the ACMG scheme |
|
formatZip |
VCF genotype fields |
|
FS |
Fisher’s exact test of read strand. If the reference reads are balanced between forward and reverse strands then the alternate reads should be as well |
|
max_af |
Maximum reported allele frequency (1000GP3, EVS, EXAC, Kyoto, GONL) |
Perspective views¶
Perspectives subtabs focus on subsets of the columns in the Default view.
Perspective |
Description |
|---|---|
ACMG |
Displays only CAT 1 and 2 variants that are Known InACMG (“True”). The following annotation columns are displayed in this perspective: DIAG_ACMGCat, max_consequence, KNOWN_Gene_diseases, and KNOWN_var diseases. |
Default view |
Displays all columns |